NORTHEAST INDIANS
Northeast Tribes
Also known as Eastern Woodland Indians
Ethnographers commonly classify indigenous peoples in the United States and Canada into ten geographical regions with shared cultural traits (called cultural areas).
The following index links to further information about the native American indian tribes included the Northeast Woodlands region. Tribes are grouped by their original culture group, but this is often not where they live today.
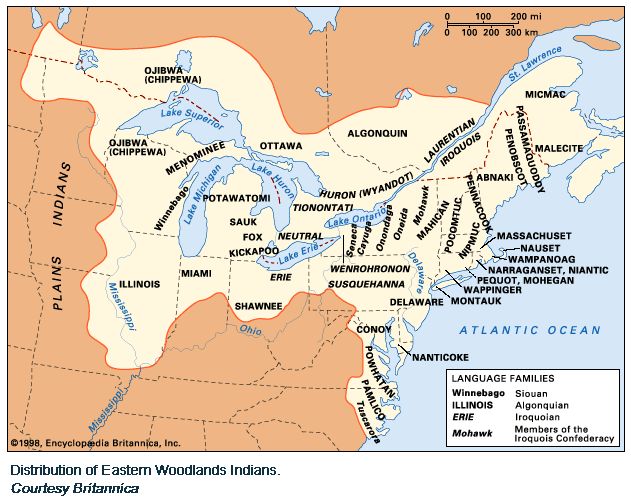
Northeast Location: Connecticut |Delaware | District of Columbia | Maine | Maryland | Massachusetts | New Hampshire | New Jersey | New York | Pennsylvania | Rhode Island | Vermont
Upper Eastern Location: Indiana | Kentucky | North Carolina | Tennessee | Virginia | West Virginia The Eastern Woodland region spreads from the Great Lakes to the North Atlantic Coast and south to the Ohio River Valley. As the name implies, this geographical area was mostly deciduous woodlands.
Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands (also known as Eastern Woodlands)include Native Americans and First Nations peoples originating from a cultural area encompassing the northeastern and Midwest United States and southeastern Canada.
The Northeastern Woodlands is divided into three major areas: the Coastal, Saint Lawrence Lowlands, and Great Lakes-Riverine zones.
The Coastal area includes the Atlantic Provinces in Canada, the Atlantic seaboard of the United States, south to North Carolina.
The Saint Lawrence Lowlands area includes parts of Southern Ontario, upstate New York, much of the Saint Lawrence River area, and Susquehanna Valley.
The Great Lakes-Riverine area includes the remaining inland areas of the northeast, home to Central Algonquian and Siouan speakers.
The Great Lakes region are sometimes considered a distinct cultural region, due to the large concentration of tribes in the area.
The Northeastern Woodlands region is bound by the Subarctic to the north, the Great Plains to the west, and the Southeastern Woodlands to the south.
Classification of indigenous peoples of the Americas is based upon cultural regions, geography, and linguistics in the late 1500s.
Anthropologists have named various cultural regions, with fluid boundaries, that are generally agreed upon with some variation.
These cultural regions are broadly based upon the locations of indigenous peoples of the Americas from early European and African contact beginning in the late 15th century.
When indigenous peoples have been forcibly removed by nation-states, they retain their original geographic classification. Some groups span multiple cultural regions.
Eastern Woodland Tribes (Northeast)
- Adena culture (1000–200 BCE) formerly Ohio, Indiana, West Virginia, Kentucky, New York, Pennsylvania and Maryland
- Abenaki (Tarrantine), Maine, Vermont, New Hampshire, Quebec, and Vermont. The Abenaki are from Ndakinna, “our land” of northern New England and southern Quebec, and are the western relatives of other Wabanaki groups in that region, including the Maine tribes of Passamaquoddy, Penobscot, Maliseet, and Mi’kmaq. Abenaki people living in traditional territory in northern New England today include extended family bands who have remained in their traditional places such as the Lake Champlain Valley (Betobagw), Lake Memphramagog (Memlawbagw), the Connecticut River Valley (Kwinitekw), and the White Mountains (Wôbiadenak); citizens of the Odanak and Wolinak First Nations in Quebec; and several formally organized tribes of related families.
- Eastern Abenaki, Quebec, Maine, and New Hampshire
- Kennebec (Caniba), Maine
- Western Abenaki: Quebec, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Vermont
- Eastern Abenaki, Quebec, Maine, and New Hampshire
- Accohannock – Maryland
- Anishinaabeg (Anishinape, Anicinape, Neshnabé, Nishnaabe) (see also Subarctic, Plains)
- Algonquin, Quebec, Ontario
- Nipissing, Ontario
- Ojibwe (Chippewa, Ojibwa), Ontario, Michigan, Minnesota, and Wisconsin
- Mississaugas, Ontario
- Saulteaux (Nakawē), Ontario
- Odawa people (Ottawa), Indiana, Michigan, Ohio, Ontario; later Oklahoma
- Potawatomi, Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Ontario, Wisconsin; later Kansas and Oklahoma
- Assateague, Maryland
- Attawandaron (Neutral), Ontario
- Beothuk, formerly Newfoundland (now extinct)
- Chowanoke, North Carolina
- Choptank people, Maryland
- Conoy, Virginia, Maryland
- Fort Ancient culture (1000-1750 CE), formerly Ohio, Kentucky, Indiana and West Virginia
- Erie, Pennsylvania, New York
- Etchemin, Maine
- Ho-Chunk (Winnebago), Wisconsin around Green Bay, northern Illinois, later Pennsylvania, Ohio, West Virginia, Iowa and Nebraska
- Honniasont, Pennsylvania, Ohio, West Virginia
- Hopewell tradition, formerly Ohio, Illinois, and Kentucky, and Black River region, 200 BCE—500 CE
- Housatonic, Massachusetts, New York
- Illinois Confederacy (Illiniwek), Illinois, Iowa, and Missouri
- Cahokia, Illinois, Iowa, Missouri, Arkansas, now Oklahoma
- Illinois,
- Kaskaskia, formerly Wisconsin
- Miami, Illinois, Indiana, and Michigan, now Oklahoma
- Mitchigamea, formerly Illinois
- Moingona, formerly Illinois
- Peoria, Illinois, now Oklahoma
- Tamaroa, formerly Illinois
- Wea, formerly Indiana, descendants in Oklahoma
- Meskwaki (Fox), Michigan, now Iowa, Oklahoma
- Iroquois Confederacy (Haudenosaunee), Ontario, Quebec, and New York
- Kickapoo, Michigan, Illinois, Missouri, now Kansas, Oklahoma, Texas, Mexico
- Laurentian (St. Lawrence Iroquoians), formerly New York, Ontario, and Quebec, 14th century—1580 CE
- Lenni Lenape (Delaware), Pennsylvania, Delaware, New Jersey, now Ontario and Oklahoma
- Munsee-speaking subgroups, formerly Long Island and southeastern New York
- Canarsie (Canarsee), formerly Long Island New York
- Esopus, formerly New York, later Ontario and Wisconsin
- Hackensack, formerly New York
- Haverstraw (Rumachenanck), New York
- Kitchawank (Kichtawanks, Kichtawank), New York
- Minisink, formerly New York
- Navasink, to the east along the north shore of New Jersey
- Raritan, formerly Westchester County, New York
- Sinsink (Sintsink), Westchester County, New York
- Siwanoy, Massachusetts
- Tappan, formerly New York
- Waoranecks
- Wappinger (Wecquaesgeek, Nochpeem), formerly New York
- Warranawankongs
- Wiechquaeskeck, formerly New Yor
- Unami-speaking subgroups
- Acquackanonk, Passaic River in northern New Jersey
- Okehocking, southeast Pennsylvania
- Unalachtigo, Delaware, New Jersey
- Manahoac, Virginia
- Mascouten, formerly Michigan
- Massachusett, Massachusetts
- Ponkapoag, Massachusetts
- Menominee, Wisconsin
- Mahican (Stockbridge Mahican) Connecticut, Massachusetts, New York, and Vermont
- Massachusett, Massachusetts
- Meherrin, Virginia, North Carolina
- Mi’kmaq (Micmac), New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, Quebec, and Maine
- Mohegan, Connecticut
- Monacan, Virginia
- Montaukett (Montauk),New York
- Monyton (Monetons, Monekot, Moheton) (Siouan), West Virginia and Virginia
- Nansemond, Virginia
- Nanticoke, Delaware and Maryland
- Accohannock
- Narragansett, Rhode Island
- Niantic, coastal Connecticut
- Nipmuc (Nipmuck), Connecticut, Massachusetts, and Rhode Island
- Nottaway, Virginia,
- Occaneechi (Occaneechee), Virginia
- Passamaquoddy, New Brunswick, and Maine
- Patuxent, Maryland
- Paugussett, Connecticut
- Potatuck, New York
- Penobscot, Maine
- Pequot, Connecticut
- Petun (Tionontate), Ontario
- Piscataway, Maryland
- Pocumtuc, western Massachusetts
- Podunk, New York, eastern Hartford County, Connecticut
- Powhatan Confederacy, Virginia
- Appomattoc, Virginia
- Arrohateck, Virginia
- Chesapeake, Virginia
- Chesepian, Virginia
- Chickahominy, Virginia
- Kiskiack, Virginia
- Mattaponi, Virginia
- Nansemond, Virginia
- Paspahegh, Virginia
- Powhatan, Virginia
- Pamunkey, Virginia
- Quinnipiac, Connecticut, eastern New York, northern New Jersey
- Rappahannock, Virginia
- Sauk (Sac), Michigan, now Iowa, Oklahoma
- Schaghticoke, western Connecticut
- Shawnee, formerly Ohio, Virginia, West Virginia, Pennsylvania, currently Oklahoma
- Shinnecock, Long Island, New York
- Stegarake, Virginia
- Stuckanox (Stukanox), Virginia
- Susquehannock, Maryland, Pennsylvania
- Tauxenent (Doeg), Virginia
- Tunxis (Massaco), Connecticut
- Tuscarora, formerly North Carolina, Virginia, currently New York
- Tutelo (Nahyssan), Virginia
- Unquachog (Poospatuck), Long Island, New York
- Wabanaki, Maine, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Quebec
- Wampanoag, Massachusetts
- Nauset, Massachusetts
- Patuxet, Massachusetts
- Pokanoket, Massachusetts, Rhode Island
- Wangunk, Mattabeset, Connecticut
- Wenro, New York
- Wicocomico, Maryland, Virginia
- Wolastoqiyik, Maliseet, Maine, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Quebec
- Wyachtonok, Connecticut, New York
- Wyandot (Huron), Ontario south of Georgian Bay, now Oklahoma, Kansas, Michigan, and Wendake, Quebec
- Munsee-speaking subgroups, formerly Long Island and southeastern New York
Acquintanacsnak
Algonkin
Algonquian – lower Saint Lawrence River
Algonquins, – Outaouais and Abitibi in Quebec, Ontario
Anishinaabe (Anishinape, Anicinape, Neshnabé, Nishnaabe) (see also Subarctic, Plains Tribes)Beothuk formerly Newfoundland, no longer exist
Arosaguntacook
Atquanachuke
Brotherton
Conestoga
Caniba
Chicora, Eastern NC South Carolina
Chowanoc in North Carolina
Congarees in North Carolina
Conoy
Coree in North Carolina
Eno, North Carolina
Erie
Etchemin, Quebec (Maliseet)
Fox
Hathawekela (Absentee Shawnee)
Hatteras
Hammonasset
The Haudenosaunee Confederacy is composed of 6 tribes that are western neighbors of the New England tribes, with territories extending beyond the modern-day international boundary separating the United States and Canada.
Honniasont
Huron/Wyandot, Ontario south of Georgian Bay, now Oklahoma and Wendake, Quebec
Illinois (Illini), Illinois
Iroquois New York
Cayuga – The homeland of the Cayuga Nation of New York lays between the Seneca and Onondaga nations.
Laurentian/St. Lawrence Iroquoians
Mohawk
Saint Regis Mohawk is the U.S.-recognized tribal group of Mohawk.
For Canadian-based Mohawks, please see the following: Mohawks of Akwesasne
Mohawks of the Bay of Quinte
Mohawks of Kahnawake
Kanesatake First Nation
Oneida -The Oneida Indian Nation of New York is known as the first ally of the United States, having fought with the colonists against the British during the American Revolution.
Onondaga – The Onondaga Nation maintains its 7,300-acre territory just south of Syracuse, NY.
Seneca – The Senecas are the western-most nation of the Haudenosaunee Confederacy. They have three reservations: the Allegany & Cattaraugus territories are part of the Seneca Nation of Indians, and the Tonawanda Senecas have their own reservation.
Tuscarora – The Tuscarora Nation reservation is located in Western New York.
Jaupin or Weapemoc. North Carolina.
Keyauwee, North Carolina
Kickapoo – Originally from Illinois, Missouri, Kansas, Oklahoma, Texas, and Mexico. Now three federally recognized tribes:
Kickapoo Traditional Tribe of Texas
Kickapoo Tribe of Indians of the Kickapoo Reservation in Kansas
Lenni-Lenape, Pennsylvania, Delaware, New Jersey, now Ontario and Oklahoma
Loup A
Loup
Machapunga in North CarolinaMaliseet, Maine, Quebec, and New Brunswick, CanadaMunseeUnamiUnalachtigo
Lumbee
Manhattan
Mahican
Malecite
Maliseet – The band of the Maliseet Indians (Maine) in the United States are federally recognized as the Houlton Band of Maliseet.
Marameg
Martha’s Vineyard Indians
Mascouten
Massachusett, Massachusetts
Mashpee
Maskegon
Matinecoc
Mattabesec or Mattabesic
Mattatuck
Meits
Menominee
Menunkatuck
Meriden (tribe)
Metoac
Meherrin
Miami, Indiana, now Oklahoma
Mioonkhtuck
Mingo, Pennsylvania, Ohio, West Virginia
Mohawk (New York)
Mohegan – The Mohegan Tribe is located in southeastern Connecticut.
Montauk New York
Moravians
Munsee
Nanticoke
Narragansett, southern Rhode Island
Natick
Nauset
Neusiok, North Carolina
Neutral
Niantic (Eastern) (Western)
Nipissing, Ontario
Nipmuc, Massachusetts – The Nipmuc Indians are the tribal group occupying the central part of Massachusetts, northeastern Connecticut and northwestern Rhode Island. The Nipmuc Nation is a state-recognized band with approximately 500 enrolled members today based at the Hassanamisco Reservation (in Grafton, MA). This small 3-acre reservation is the only parcel of Nipmuc land never to have changed hands; its occupation by Nipmuc people dates back to before contact and colonization. The Nipmuc Indians of Massachusetts have several bands today, including the Chaubunagungamaug of Webster and Natick Nipmuc of Natick, in addition to the Nipmuc Nation.
Nottaway, North Carolina
Ocaneechee
Ojibwa (Chippewa, Ojibwe) Ontario, Michigan, Wisconsin, Minnesota
Ottawa (Odawa), Ontario, Michigan
Mississaugas, Ontario
Montauk, New York
Naugatuck (people)
Nehantic
Oji-Cree
Onondaga
Ontonagon
Ottawa
Pamlico
Pasquotank
Passamaquoddy, Maine
Pee Dee (tribe)
Pennacook
Penobscot, Maine – The Penobscot Nation of Maine is one of the four
Northeastern woodlands tribes of the Wabanaki Confederacy.
Pequawket
Eastern Pequot Nation, located in southeastern Connecticut, is currently a state-recognized tribe with a reservation in North Stonington.
Mashantucket Pequot Nation, Connecticut – The Mashantucket Pequot Nation of Southeastern Connecticut resides on one of the oldest continuously occupied Indian reservations in America.
Its tribal symbol is a fox, which stands as a vigilant reminder of the turbulent times they went through when Europeans first arrived in the early 17th century.
The Pequot Nation was the first Native American group within United States to suffer an attempted genocide by Puritan colonists in 1637 (the Pequot War).
Paugusset (Connecticut)
The Golden Hill Paugussett have one of the oldest and smallest reservations in the country. Established in 1659, today the reservation is approximately ¼ of an acre, large enough for Chief Aurelius Pipers’ family.
In 1659, the General Court of Hartford decided that the colonists had the right to take Paugussett lands, which became the city of Bridgeport. In return, the Indians were to receive an 80-acre tract of land known as “Golden Hill” which was granted “forever.”
But the stealing of Paugussett land continued. Finally, in 1875 William Sherman purchased a 1/4 acre of land in Trumbull and gave it to the overseer to be held in trust for the Tribe forever.
In 1939 the Attorney General wrote an opinion that the property was Tribal land for the Golden Hill people.
Peoria Illinois, now Oklahoma
Petun
Piankashaw
Piscataway-Conoy
Pocomtic
Pocumtuk
Podunk (people)
Pokanoket Tribe of the Wampanoag Nation – Rhode Island and Massachusetts
Ponkapoag
Poospatuck, New York
Potatuck
Potawatomi, Ontario, Michigan, Indiana, Wisconsin
Potoskeet, North Carolina
Powhatan, Virginia
Quinnipiac, Connecticut, eastern New York, northern New Jersey, Long Island
Quiripi
Ramapough Mountain Indians New Jersey
Saconnet
Saluda
Santee of South Carolina
Saponi, Virginia and North Carolina
Sauk (now part of the Sac and Fox tribe)originally Great Lakes now Kansas, Oklahoma, Iowa
Saulteaux (Nakawē), Ontario
Schaghticoke, Western Connecticut – The Schaghticoke Tribal Nation has been recognized by the Colony and then the State of Connecticut as a separate and distinct American Indian tribal entity continually from historic time through the 20th century.
Today, the Tribe has approximately 300 members. The historical and spiritual base of the Schaghticoke Tribal Nation is the Tribe’s approximately 400-acre reservation in Kent, Connecticut.
The reservation is mountainous and rocky, with a small strip of flatland located on a flood plain along the Housatonic River.
Secotan
Sewee
Shawnee Ohio, West Virginia, Pennsylvania [most ended up in Oklahoma]
Shakori, North Carolina
Shinnecock New York – The Shinnecock Indian Nation is located along the eastern shores of Long Island.
Sissipahaw
Souriquoian
Sugaree
Susquahannock
Susquehanna
Tarrantine or Tarranteen – See Abenaki, or Micmac
Tionontati
Totoket
Tunxis
Tutelo
Tunxis
Unalachtigo
Unami
Unquachog – The Unkechaug (“people from beyond the hill”) Indian Nation is based in New York, centered around the 55-acre Poospatuck (“where the waters meet”) Reservation on Long Island, N.Y.
The church on the reservation is New York State’s oldest Mission church and is multi-denominational.
Unkechaug territory is particularly noted for producing what is known as “black wampum,” the dark purple associated with certain parts of Long Island.
Waccamaw
Wampanoag, Massachusetts –
The Mashpee Wampanoag Tribe is located on Cape Cod, Massachusetts.
The Wampanoag Tribe of Gay Head (Aquinnah) is based on Martha’s Vineyard.
Other Wampanoag groups include the Assonet Band, Herring Pond, Seaconke, and Pocasset.
Wangunk
Wappinger
Wateree
Wawenoc
Waxhaw in North Carolina and South Carolina
Wea
Wenro
Wenrohronon, Pennsylvania and New York
Wepawaug
Woccon
Wyandot (Wyandotte,Wendat, Huron) Ontario, Michigan
Wendake, Quebec
Arctic | California | Northeast | Great Basin | Great Plains
NW Coast | Plateau | Southeast | Southwest | Sub Arctic
Subcategories
- Abenaki Indians
- Algonquin Indians
- Delaware / Lenape
- Ho-Chunk / Winnebago
- Huron / Wyandot
- Illinois Indians
- Iroquois Indians
- Kickapoo Indians
- Mahican Indians
- Maliseet Indians
- Menominee Indians
- Miami Indians
- Mikmaq Indians
- Mohegan Indians
- Munsee Indians
- Narragansett Indians
- Nipmuck Indians
- Ojibwa / Chippewa
- Passamaquoddy
- Pennacook Indians
- Penobscot Indians
- Pequot Indians
- Powhatan Indians
- Sac & Fox Nation
- Shawnee Indians
- Shinnecock Indians
- Wampanoag Indians
Article Index:
Seventeen American Indian tribes originated around the Great Lakes Region, and later migrated to other areas. Here is a summary of those tribes. Meaning of the tribal name is in brackets, where known.

